SUIT-028: Difference between revisions
From Bioblast
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{MitoPedia | {{MitoPedia | ||
|abbr=NS(PGM) | |abbr=NS(PGM) | ||
|description=[[File:1PGM;2D;3S;4U;5Rot-.png|400px]] | |description=[[File:1PGM;2D;3S;4U;5Rot-.png|400px|SUIT-028]] | ||
|info='''C''' [[MiPNet18.13 IOC84 Alaska]] | |info='''C''' [[MiPNet18.13 IOC84 Alaska]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{MitoPedia concepts | |||
|mitopedia concept=MiP concept, SUIT protocol, SUIT C | |||
}} | |||
{{MitoPedia methods | |||
|mitopedia method=Respirometry | |||
}} | |||
{{MitoPedia O2k and high-resolution respirometry}} | |||
{{MitoPedia topics}} | |||
::: '''[[SUIT protocol pattern]]:''' 1PGM;2D;3S;4U;5Rot- | ::: '''[[SUIT protocol pattern]]:''' 1PGM;2D;3S;4U;5Rot- | ||
| Line 74: | Line 82: | ||
|} | |} | ||
{{ | == References == | ||
| | {{#ask:[[Category:Publications]] [[Instrument and method::O2k-Protocol]] [[Additional label::SUIT-028]] | ||
|?Was published in year=Year | |||
|?Has title=Reference | |||
| | |?Mammal and model=Organism | ||
|?Tissue and cell=Tissue;cell | |||
|format=broadtable | |||
|limit=5000 | |||
|offset=0 | |||
|sort=Was published in year | |||
|order=descending | |||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 10:30, 26 February 2020
Description
Abbreviation: NS(PGM)
Reference: C MiPNet18.13 IOC84 Alaska
MitoPedia concepts:
MiP concept,
SUIT protocol,
SUIT C
MitoPedia methods:
Respirometry
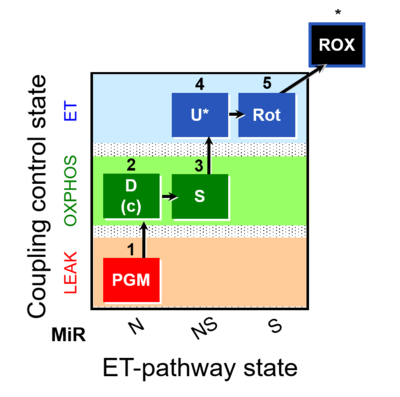
- SUIT protocol pattern: 1PGM;2D;3S;4U;5Rot-
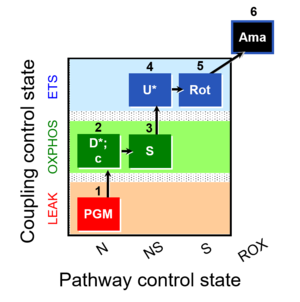
1PGM;2D;2c;3S;4U;5Rot;6Ama
| Step | Respiratory state | Pathway control | Pathway to Q | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1PGM | PGM(L) | N | CI | LEAK state with type N substrates, NL: Non-phosphorylating resting state with NADH-linked (type N) substrates pyruvate&glutamate&malate (PGM; without adenalytes; CI-linked pathway to Q). See 2D.
|
| 2D | PGM(P) | N | CI | OXPHOS capacity with type N substrates, NP: Respiratory capacity in the active coupled state (PGM with ADP). PGM ensures a higher N-pathway flux, if PM- or GM-pathway capacity is lower than PGM. Compared to PM, the contribution of the S-pathway may be higher with PGM. Compare 1PM;2D;3U;4S;5Rot- and 1PM;2D;3U;4G;5S;6Oct;7Rot;8Gp- . |
| D(c) | PGM(c) | N | CI | Cytochrome c test for quality control of the integrity of the outer mitochondrial membrane (loss of cytochrome c is indicated by a stimulation of respiration). Cytochrome c added immediately after the earliest ADP-activation step. Application of the cytochrome c test early in the protocol ensures comparability of all states in case of any effect of c (Gnaiger 2007 MitoPathways). |
| 3S | PGMS(P) | NS | CI&II | OXPHOS capacity with type NS substrates (CI&II-linked pathway to Q), NSP: Respiratory stimulation by convergent electron flow through Complexes I&II at the Q-junction, in the coupled state after further addition of succinate (S), as an estimate of OXPHOS capacity with reconstitution of the TCA cycle (Gnaiger 2009 Int J Biochem Cell Biol). |
| 4U | PGMS(E) | NS | CI&II | electron transfer-pathway (ET-pathway) capacity with type NS substrates, NSE: Uncoupling by CCP or FCCP titration (avoiding inhibition by high uncoupler concentrations), as a test for limitation of OXPHOS relative to ET capacity by the phosphorylation system. Limitation: The additive effect of N+S measured separately compared to the combined NS pathway cannot be evaluated in the same coupling state. With NP, NSP, NSE, and SE. If independent information is available on SP = SE, the additivity can be calculated for the OXPHOS state. |
| 5Rot | S(E) | S | CII | ET capacity with type S (CII) substrate, SE: ET capacity with succinate, after blocking Complex I with rotenone. Limitation: A succinate concentration of >10 mM may be required for saturating SE capacity. |
| 6Ama | ROX | Residual oxygen consumption (ROX) due to oxidative side reactions, estimated after addition of antimycin A (inhibitor of Complex III). ROX may be lower in substrate states earlier in the SUIT protocol. Therefore, this ROX measurement is frequently taken as a methodological control rather than as the final basis of ROX correction of mitochondrial respiration (mt). |