Description
Abbreviation: NS_1GM,2D,3S,4U,5Rot-
Reference: B MiPNet12.23 FibreRespiration
MitoPedia concepts:
SUIT protocol,
SUIT B
- SUIT-catg: NS(GM)
- SUIT protocol pattern: diametral
- Mark names in DatLab: SUIT_NS(GM)01
- DatLab-Analysis template: SUIT_NS(GM)01.xlsx
SUIT_NS(GM)01_D(c)
| Step | Respiratory state | Pathway control | Pathway to Q | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
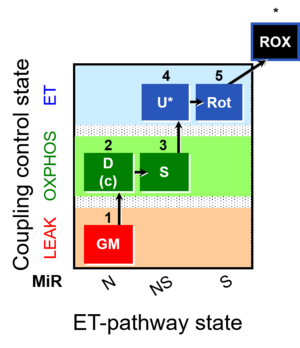
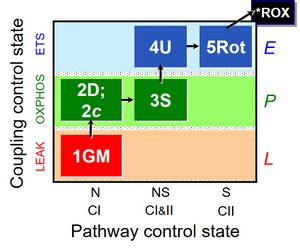
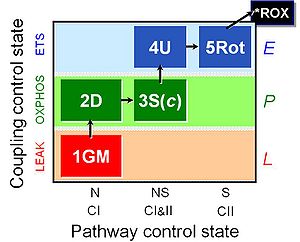
| 1GM | GM(L) | N | CI | LEAK state with type N substrates, NL: Non-phosphorylating resting state with NADH-linked (type N) substrates glutamate&malate (GM; without adenalytes; CI-linked pathway to Q). See 2D.
|
| 2D | GM(P) | N | CI | OXPHOS capacity with type N substrates, NP: Respiratory capacity in the active coupled state (GM with ADP). GM and PM yield practically identical fluxes in human skeletal muscle fibres. However, PM is the superior alternative to GM, since the fractions of the N-pathway is lower and of the S-pathway is higher with GM compared to PM. PM, therefore, yields a more sensitive assay for the diagnosis of injuries in the N-linked (CI-linked) pathway. Compare SUIT_NS(PM)01 and SUIT_RP1. |
| D(c) | GM(c) | N | CI | Cytochrome c test for quality control of the integrity of the outer mitochondrial membrane (loss of cytochrome c is indicated by a stimulation of respiration). Cytochrome c added immediately after the earliest ADP-activation step. Application of the cytochrome c test early in the protocol ensures comparability of all states in case of any effect of c (Gnaiger 2007 MitoPathways). |
| 3S | GMS(P) | NS | CI&II | OXPHOS capacity with type NS substrates (CI&II-linked pathway to Q), NSP: Respiratory stimulation by convergent electron flow through Complexes I&II at the Q-junction, in the coupled state after further addition of succinate (S), as an estimate of OXPHOS capacity with reconstitution of the TCA cycle (Gnaiger 2009 Int J Biochem Cell Biol). |
| 4U | GMS(E) | NS | CI&II | Electron transfer system (ETS) capacity with type NS substrates, NSE: Uncoupling by CCP or FCCP titration (avoiding inhibition by high uncoupler concentrations), as a test for limitation of OXPHOS relative to ETS capacity by the phosphorylation system. Limitation: The additive effect of N+S measured separately compared to the combined NS pathway cannot be evaluated in the same coupling state. With NP, NSP, NSE, and SE. If independent information is available on SP = SE, the additivity can be calculated for the OXPHOS state. |
| 5Rot | S(E) | S | CII | ETS capacity with type S (CII) substrate, SE: ETS capacity with succinate, after blocking Complex I with rotenone. Limitation: A succinate concentration of >10 mM may be required for saturating SE capacity. |
| 6Ama | ROX | ROX | Residual oxygen consumption (ROX) due to oxidative side reactions, estimated after addition of antimycin A (inhibitor of Complex III). ROX may be lower in substrate states earlier in the SUIT protocol. Therefore, this ROX measurement is frequently taken as a methodological control rather than as the final basis of ROX correction of mitochondrial respiration (mt). |