Template:Keywords: Coupling control: Difference between revisions
From Bioblast
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
! Respiratory rate !! Definition !! Icon | ! Respiratory rate !! Definition !! Icon | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[OXPHOS | | [[OXPHOS capacity]] || ''P'' = ''P´''-''Rox'' || [[File:P.jpg |link=OXPHOS capacity]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[ROUTINE | | [[ROUTINE respiration]] || ''R'' = ''R´''-''Rox'' || [[File:R.jpg |link=ROUTINE respiration]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[ET | | [[ET capacity]] || ''E'' = ''E´''-''Rox'' || [[File:E.jpg |link=ET capacity]] || » [[Level flow]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| || || || » [[Noncoupled respiration]] - [[Uncoupler]]<ref>Gnaiger E. Is respiration uncoupled - noncoupled - dyscoupled? Mitochondr Physiol Network. »[[Uncoupler]]«</ref> | | || || || » [[Noncoupled respiration]] - [[Uncoupler]]<ref>Gnaiger E. Is respiration uncoupled - noncoupled - dyscoupled? Mitochondr Physiol Network. »[[Uncoupler]]«</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[LEAK | | [[LEAK respiration]] || ''L'' = ''L´''-''Rox'' || [[File:L.jpg |link=LEAK respiration]] || » [[Static head]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| || || || » [[LEAK | | || || || » [[LEAK state with ATP]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| || || || » [[LEAK | | || || || » [[LEAK state with oligomycin]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| || || || » [[LEAK | | || || || » [[LEAK state without adenylates]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Residual oxygen consumption]] ''Rox'' || ''L'' = ''L´''-''Rox'' || [[File:ROX.jpg |link=Residual oxygen consumption]] | | [[Residual oxygen consumption]] ''Rox'' || ''L'' = ''L´''-''Rox'' || [[File:ROX.jpg |link=Residual oxygen consumption]] | ||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
! Respiratory net rate !! Definition !! Icon | ! Respiratory net rate !! Definition !! Icon | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Net OXPHOS | | [[Net OXPHOS capacity P-L |Net OXPHOS capacity ''P-L'']] || ''P-L'' || [[Image:P-L.jpg|50 px|link=Net OXPHOS capacity P-L |Net OXPHOS capacity ''P-L'']] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Net ROUTINE | | [[Net ROUTINE activity R-L |Net ROUTINE activity ''R-L'']] || || [[Image:R-L.jpg|50 px|link=Net ROUTINE activity R-L |Net ROUTINE activity ''R-L'']] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Net ET | | [[Net ET capacity E-L |Net ET capacity ''E-L'']] || ''E-L'' || [[Image:E-L.jpg|50 px|link=Net ET capacity E-L |Net ET capacity ''E-L'']] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[ET-excess capacity E-P |ET-excess capacity ''E-P'']] || ''E-P'' || [[Image:E-P.jpg|60 px|link=ET-excess capacity E-P |ET-excess capacity ''E-P'']] | | [[ET-excess capacity E-P |ET-excess capacity ''E-P'']] || ''E-P'' || [[Image:E-P.jpg|60 px|link=ET-excess capacity E-P |ET-excess capacity ''E-P'']] | ||
Revision as of 23:49, 10 November 2020
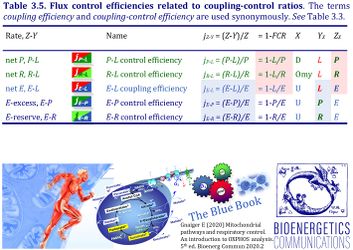
4-compartmental OXPHOS model. (1) ET capacity E of the noncoupled electron transfer system ETS. OXPHOS capacity P is partitioned into (2) the dissipative LEAK component L, and (3) ADP-stimulated P-L net OXPHOS capacity. (4) If P-L is kinetically limited by a low capacity of the phosphorylation system to utilize the protonmotive force pmF, then the apparent E-P excess capacity is available to drive coupled processes other than phosphorylation P» (ADP to ATP) without competing with P».
- Bioblast links: Coupling control - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
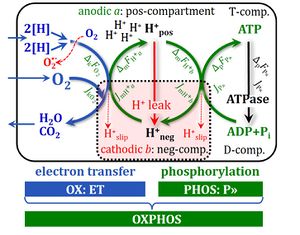
Mitochondrial and cellular respiratory rates in coupling-control states
| Respiratory rate | Definition | Icon | |
|---|---|---|---|
| OXPHOS capacity | P = P´-Rox | ||
| ROUTINE respiration | R = R´-Rox | ||
| ET capacity | E = E´-Rox | » Level flow | |
| » Noncoupled respiration - Uncoupler[1] | |||
| LEAK respiration | L = L´-Rox | » Static head | |
| » LEAK state with ATP | |||
| » LEAK state with oligomycin | |||
| » LEAK state without adenylates | |||
| Residual oxygen consumption Rox | L = L´-Rox | 
|
| FCR | Definition | Icon | |
|---|---|---|---|
| L/P coupling-control ratio | L/P | » Respiratory acceptor control ratio, RCR = P/L | |
| L/R coupling-control ratio | L/R | ||
| L/E coupling-control ratio | L/E | » Uncoupling-control ratio, UCR = E/L | |
| P/E control ratio | P/E | ||
| R/E control ratio | R/E | ||
| net P/E control ratio | (P-L)/E | ||
| net R/E control ratio | (R-L)/E |
Net, excess, and reserve capacities of respiration
| Respiratory net rate | Definition | Icon |
|---|---|---|
| Net OXPHOS capacity P-L | P-L | |
| Net ROUTINE activity R-L | ||
| Net ET capacity E-L | E-L | |
| ET-excess capacity E-P | E-P | |
| ET-reserve capacity E-R | E-R |
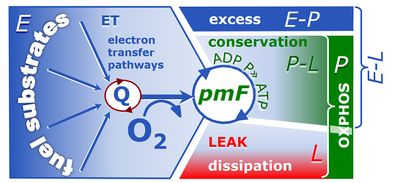
| Coupling-control efficiency | Definition | Icon | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OXPHOS-coupling efficiency P-L | jP-L | = (P-L)/P | = 1-L/P | » Biochemical coupling efficiency | |
| ROUTINE-coupling efficiency R-L | jR-L | = (R-L)/R | = 1-L/R | ||
| ET-coupling efficiency E-L | jE-L | = (E-L)/E | = 1-L/E | » Biochemical coupling efficiency | |
| ET-excess control efficiency E-P | jE-P | = (E-P)/E | = 1-P/E | ||
| ET-reserve control efficiency E-R | jE-R | = (E-R)/E | = 1-R/E |
General