Boushel 2007 Diabetologia
| Boushel RC, Gnaiger E, Schjerling P, Skovbro M, Kraunsoee R, Dela F (2007) Patients with Type 2 diabetes have normal mitochondrial function in skeletal muscle. Diabetologia 50:790-6. |
Boushel RC, Gnaiger E, Schjerling P, Skovbro M, Kraunsoee R, Dela F (2007) Diabetologia
Abstract: Aims/hypothesis: Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes are associated with mitochondrial dysfunction. The aim of the present study was to test the hypothesis that oxidative phosphorylation and electron transport capacity are diminished in the skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetic subjects, as a result of a reduction in the mitochondrial content. Materials and methods: The O2 flux capacity of permeabilised muscle fibres from biopsies of the quadriceps in healthy subjects (n=8; age 58±2 years [mean±SEM]; BMI 28±1 kg/m2; fasting plasma glucose 5.4±0.2 mmol/l) and patients with type 2 diabetes (n=11; age 62±2 years; BMI 32±2 kg/m2; fasting plasma glucose 9.0±0.8 mmol/l) was measured by high-resolution respirometry.
Results: O2 flux expressed per mg of muscle (fresh weight) during ADP-stimulated state 3 respiration was lower ( p<0.05) in patients with type 2 diabetes in the presence of complex I substrate (glutamate) (31±2 vs 43±3 pmol O2 s-1 mg-1) and in response to glutamate + succinate (parallel electron input from complexes I and II) (63±3 vs 85±6 pmol s-1 mg-1). Further increases in O2 flux capacity were observed in response to uncoupling by FCCP, but were again lower ( p<0.05) in type 2 diabetic patients than in healthy control subjects (86±4 vs 109±8 pmol s-1 mg-1). However, when O2 flux was normalised for mitochondrial DNA content or citrate synthase activity,there were no differences in oxidative phosphorylation or electron transport capacity between patients with type 2 diabetes and healthy control subjects.
Conclusions/interpretation: Mitochondrial function is normal in type 2 diabetes. Blunting of coupled and uncoupled respiration in type 2 diabetic patients can be attributed to lower mitochondrial content. • Keywords: Diabetes, Mitochondria, Skeletal muscle • Bioblast editor: Gnaiger E • O2k-Network Lab: DK Copenhagen Dela F, AT Innsbruck Gnaiger E, SE Stockholm Boushel RC, CA Vancouver Boushel RC, DK Copenhagen Larsen S
SUIT protocol
- » SUIT-011
Corrections
- Some concentrations of substrates applied in the respirometric protocols are reported in this publication to have been higher than in MiPNet09.12, but actually the concentrations have been applied according to MiPNet09.12.
MitoEAGLE VO2max/BME database
- Human vastus lateralis
- 8 males
- 58 years
- Western sedentary lifestyle, routine activities (walking, gardening..), not engaged in regular structured aerobic or strength training programmes or athletics; non-diabetic controls
- H = 1.79 m
- M = 90 kg
- BME = 0.34
- BMI = 28.1 kg·m-2
- VO2max/M = 31.2 mL·min-1·kg-1
- Permeabilized muscle fibres; 37 °C; GMSP; mw
- JO2,P(NS) = 85.4 µmol·s-1·kg-1 wet muscle mass
- Human vastus lateralis
- 11 males
- 62 years
- T2 Diabetic patients
- H = 1.77 m
- M = 100.5 kg
- BME = 0.55
- BMI = 32.1 kg·m-2
- VO2max/M
- Permeabilized muscle fibres; 37 °C; GMSP; mw
- JO2,P(NS) = 63.5 µmol·s-1·kg-1 wet muscle mass
References: BME and VO2max
- » VO2max
| Reference | |
|---|---|
| Bakkman 2007 ActaPhysiol | Bakkman L, Sahlin K, Holmberg HC, Tonkonogi M (2007) Quantitative and qualitative adaptation of human skeletal muscle mitochondria to hypoxic compared with normoxic training at the same relative work rate. Acta Physiol (Oxford) 190:243–51. |
| Boushel 2007 Diabetologia | Boushel RC, Gnaiger E, Schjerling P, Skovbro M, Kraunsoee R, Dela F (2007) Patients with Type 2 diabetes have normal mitochondrial function in skeletal muscle. Diabetologia 50:790-6. |
| Chambers 2020 J Appl Physiol (1985) | Chambers TL, Burnett TR, Raue U, Lee GA, Finch WH, Graham BM, Trappe TA, Trappe S (2020) Skeletal muscle size, function, and adiposity with lifelong aerobic exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985) 128:368–78. |
| Daussin 2008 Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol | Daussin FN, Zoll J, Dufour SP, Ponsot E, Lonsdorfer-Wolf E, Doutreleau S, Mettauer B, Piquard F, Geny B, Richard R (2008) Effect of interval versus continuous training on cardiorespiratory and mitochondrial functions: relationship to aerobic performance improvements in sedentary subjects. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 295:R264-72. |
| Garnier 2005 FASEB J | Garnier A, Fortin D, Zoll J, N'Guessan B, Mettauer B, Lampert E, Veksler V, Ventura-Clapier R (2005) Coordinated changes in mitochondrial function and biogenesis in healthy and diseased human skeletal muscle. FASEB J 19:43-52. |
| Gnaiger 2015 Scand J Med Sci Sports | Gnaiger E, Boushel R, Søndergaard H, Munch-Andersen T, Damsgaard R, Hagen C, Díez-Sánchez C, Ara I, Wright-Paradis C, Schrauwen P, Hesselink M, Calbet JAL, Christiansen M, Helge JW, Saltin B (2015) Mitochondrial coupling and capacity of oxidative phosphorylation in skeletal muscle of Inuit and caucasians in the arctic winter. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.12612 |
| Gnaiger 2019 MiP2019 | OXPHOS capacity in human muscle tissue and body mass excess – the MitoEAGLE mission towards an integrative database (Version 6; 2020-01-12). |
| Loe 2013 PLOS ONE | Loe H, Rognmo Ø, Saltin B, Wisløff U (2013) Aerobic capacity reference data in 3816 healthy men and women 20-90 years. PLOS ONE 8:e64319. |
| Mettauer 2001 J Am Coll Cardiol | Mettauer B, Zoll J, Sanchez H, Lampert E, Ribera F, Veksler V, Bigard X, Mateo P, Epailly E, Lonsdorfer J, Ventura-Clapier R (2001) Oxidative capacity of skeletal muscle in heart failure patients versus sedentary or active control subjects. J Am Coll Cardiol 38:947-54. |
| Mogensen 2006 J Physiol | Mogensen M, Bagger M, Pedersen PK, Fernström M, Sahlin K (2006) Cycling efficiency in humans is related to low UCP3 content and to type I fibres but not to mitochondrial efficiency. J Physiol 571:669-81. |
| N'Guessan 2004 Mol Cell Biochem | N'Guessan B, Zoll J, Ribera F, Ponsot E, Lampert E, Ventura-Clapier R, Veksler V, Mettauer B (2004) Evaluation of quantitative and qualitative aspects of mitochondrial function in human skeletal and cardiac muscles. Mol Cell Biochem 256-257:267-80. |
| Pesta 2011 Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol | Pesta D, Hoppel F, Macek C, Messner H, Faulhaber M, Kobel C, Parson W, Burtscher M, Schocke M, Gnaiger E (2011) Similar qualitative and quantitative changes of mitochondrial respiration following strength and endurance training in normoxia and hypoxia in sedentary humans. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 301:R1078–87. |
| Ponsot 2006 J Appl Physiol (1985) | Ponsot E, Dufour SP, Zoll J, Doutrelau S, N'Guessan B, Geny B, Hoppeler H, Lampert E, Mettauer B, Ventura-Clapier R, Richard R (2006) Exercise training in normobaric hypoxia in endurance runners. II. Improvement of mitochondrial properties in skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985) 100:1249-57. |
| Pribis 2010 Nutrients | Pribis P, Burtnack CA, McKenzie SO, Thayer J (2010) Trends in body fat, body mass index and physical fitness among male and female college students. Nutrients 2:1075-85. |
| Raboel 2009 Diabetes Obes Metab | Raboel R, Hojberg PM, Almdal T, Boushel RC, Haugaard SB, Madsbad S, Dela F (2009) Improved glycaemic control decreases inner mitochondrial membrane leak in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 11:355-60. |
| Rasmussen 2001 Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab | Rasmussen UF, Rasmussen HN, Krustrup P, Quistorff B, Saltin B, Bangsbo J (2001) Aerobic metabolism of human quadriceps muscle: in vivo data parallel measurements on isolated mitochondria. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 280:E301-7. |
| Rasmussen 2003 Eur J Physiol | Rasmussen UF, Krustrup P, Kjaer M, Rasmussen HN (2003) Human skeletal muscle mitochondrial metabolism in youth and senescence: no signs of functional changes in ATP formation and mitochondrial oxidative capacity. Pflugers Arch – Eur J Physiol 446:270-78. |
| Zoll 2002 J Physiol | Zoll J, Sanchez H, N'Guessan B, Ribera F, Lampert E, Bigard X, Surrurier B, Fortin D, Geny B, Veksler V, Ventura-Clapier R, Mettauer B (2002) Physical activity changes the regulation of mitochondrial respiration in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 543:191-200. |
Labels: MiParea: Respiration, mt-Biogenesis;mt-density, mt-Medicine
Pathology: Diabetes, Obesity
Organism: Human Tissue;cell: Skeletal muscle Preparation: Permeabilized tissue
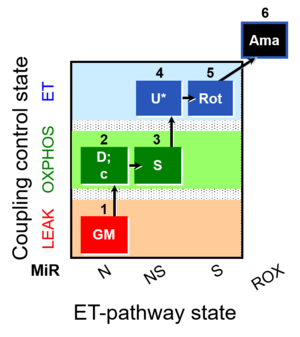
Regulation: Coupling efficiency;uncoupling, Substrate Coupling state: LEAK, OXPHOS, ET Pathway: N, S, NS HRR: Oxygraph-2k
SUIT-011, BMI, VO2max, BME, MitoEAGLE BME